The Purpose: The Flexible Box Layout Module, makes it easier to design a flexible responsive layout structure without using float or positioning. It's a more efficient way to layout, align, and distribute space among items in a container.
/* This creates a flex container and all elements inside this
container become 'flex items'. */
.flex-container {
display: flex;
}
Terminology
- Flex container: refers to the element that has the
display: flexproperty applied to it. - Flex items: refers to the elements that are contained within a flex-container.
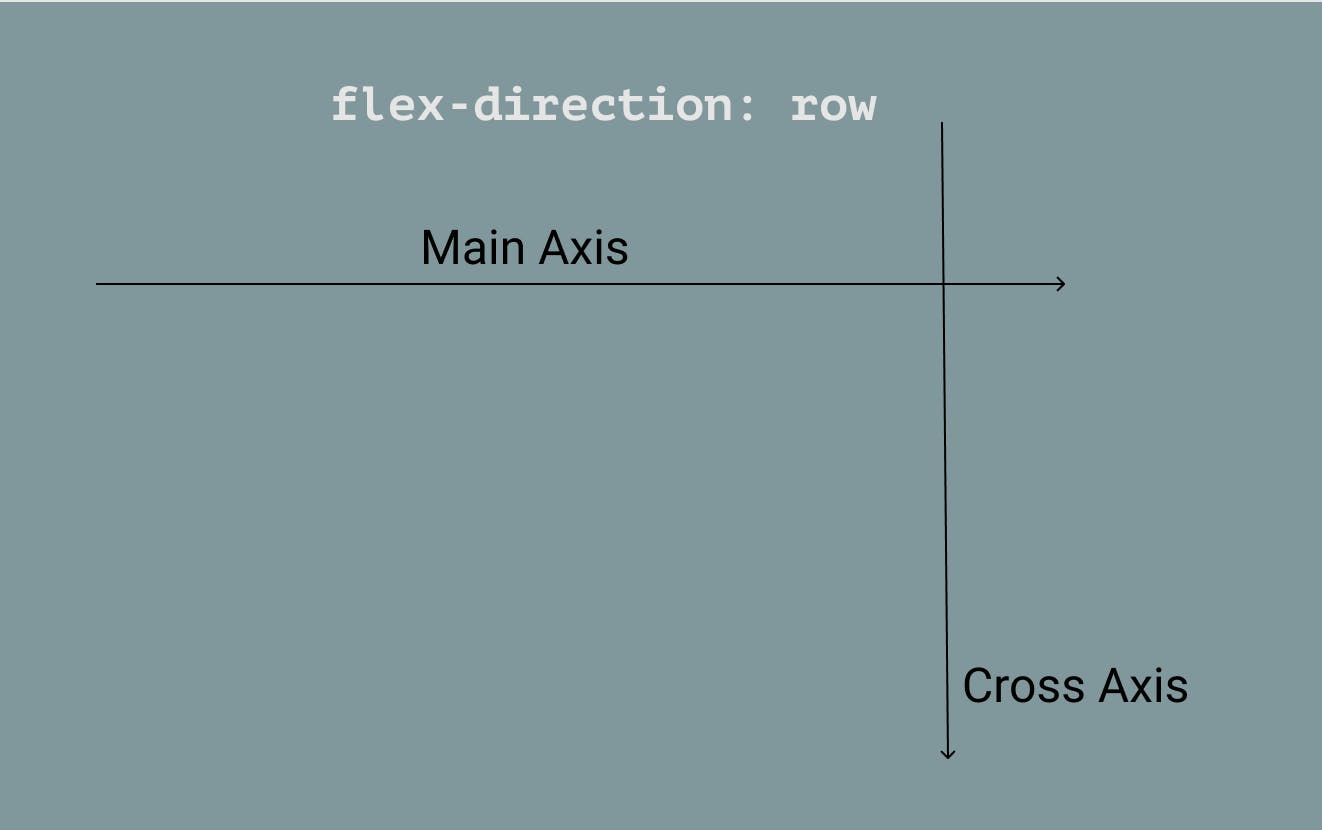
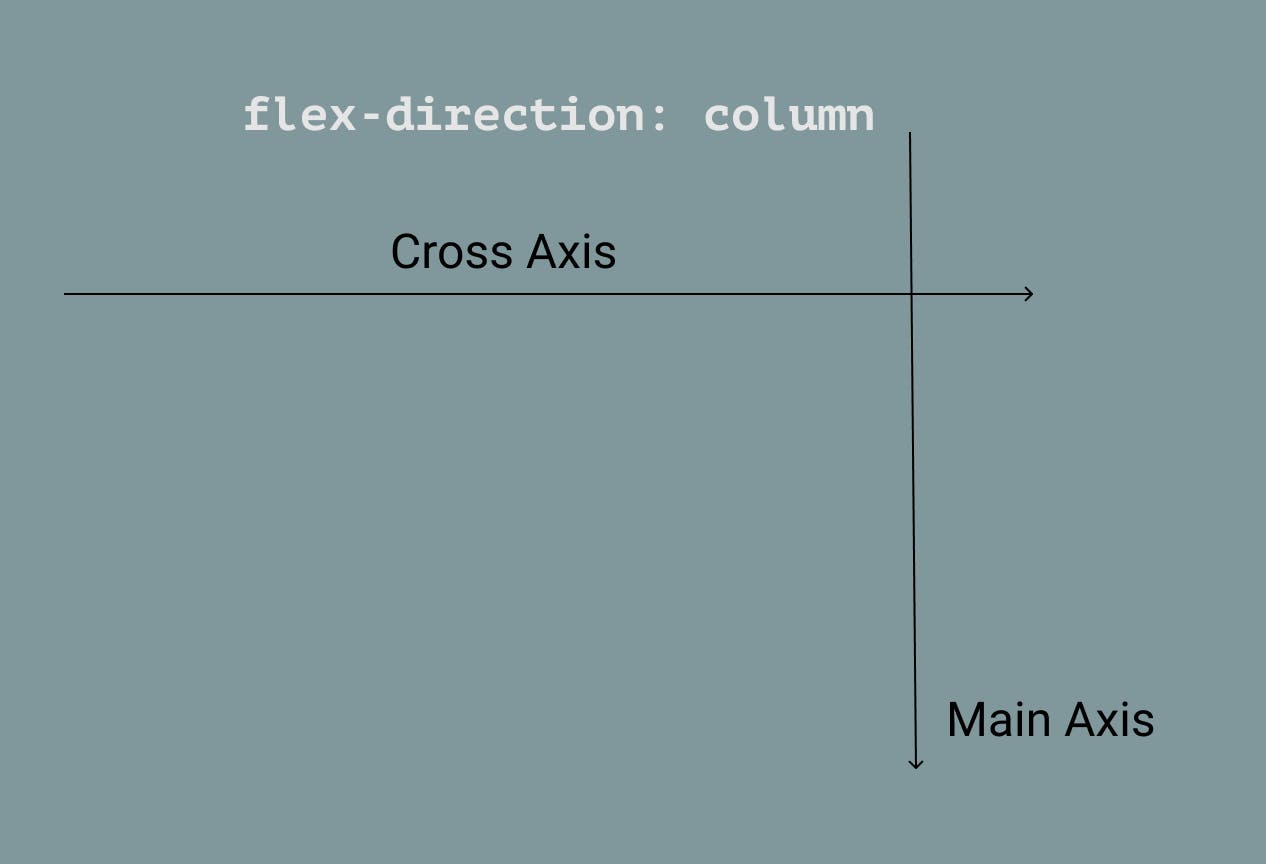
- Main axis: By default, the main axis direction goes from left to right. You can change the direction of the main axis with
flex-direction. - Cross axis: is the opposite of whatever the main axis is. By default, the direction of it goes from top to bottom.
💡 The main axis and cross axis will always be perpendicular to one another.
Container Properties
flex-directionflex-wrapjustify-contentalign-itemsalign-content
1) flex-direction
- Allows us to specify how flex items are placed within a flex container. It defines the main axis and its direction. Default is
flex-direction: row. - When
flex-direction: rowis applied, the main axis is horizontal. - When
flex-direction: columnis applied, the main axis is vertical. - Sandbox Examples 🏗️
2) flex-wrap
- Allows us to specify if the items in a flex container (flex items) are forced into a single line or can be wrapped into multiple lines. Default is
flex-wrap: nowrap. This applies to both rows and columns (although columns are less common and look a little wonky.) - If
flex-wrapis not defined on a container and you have elements with large widths, the flexbox container will ignore them and make it so that everything fits on a single line. The container will make the items as big as they can without making them wrap. - Sandbox Examples 🏗️
3) justify-content
- Allows us to specify how the space inside of a flex container should be distributed between the different items along the main axis.
- Default is
justify-content: flex-start - Sandbox Examples 🏗️
4) align-items
- Defines how space is distributed between items in flex container along the cross axis. Default is
align-items: stretch. justify-contentandalign-itemsdo the same things, just on different axes.- Sandbox Examples 🏗️
5) align-content
- Defines how space is distributed between rows in a flex container along the cross axis. Default is
align-content: stretch. - Sandbox Examples 🏗️
Flex-Item Properties
align-selforderflex-basisflex-shrinkflex-growflex
1) align-self
- Allows you to override
align-itemson an individual flex item. Default isalign-self: auto. - It’s very similar to
align-items. Whilealign-itemsencompasses all flex items in a container,align-selfgrabs an individual flex item and applies the property to that individual item only along the cross axis. - Sandbox Examples 🏗️
2) order
- Specifies the order used to layout items in their flex container.
- By default, all items have an order of 0.
orderonly affects the visual order of items and not their logical order. Due to this, it could cause accessibility issues with screen readers since it creates a disconnect between what the user sees and the actual DOM order.
3) flex-basis
- Specifies the ideal size of a flex item before it’s placed into a flex-container.
- It’s sort of like width when you are working with rows and height when you’re working with columns.
- For example, If you were to have a row with a set
widthandflex-basis, theflex-basisvalue would get precedence over thewidthsince it’s the “ideal size.” - The Difference between width and flex-basis
- For example, If you were to have a row with a set
4) flex-shrink
- Dictates how items should shrink when there is not enough space in a container. By default,
flex-shrink: 1is applied and all items will shrink at the same rate. - The math for
flex-shrinkis different fromflex-grow. - This property can be useful for things like navigation bars where you want things to shrink in a particular way.
- MDN - flex-shrink
5) flex-grow
- Dictates how the unused space (if any) should be spread amongst flex items. By default,
flex-grow: 0is applied and all items will grow at the same rate. - When you assign a number to
flex-grow, all items will evenly divide the unused space amongst themselves. - Article on flex-grow
6) flex
- Defines how a flex item will grow or shrink to fit the available space in a container. It is a shorthand property for
flex-grow,flex-shrink, andflex-basis.- Syntax:
flex: <flex-grow> <flex-shrink> <flex-basis>
- Syntax:
- MDN - CSS flex Property
References
- Udemy Course - The Advanced Web Developer Bootcamp
- W3Schools - CSS Flexbox
- In-depth Tutorial on Flexbox by Colt Steele
[Photo by Andrew Schultz on Unsplash ]

